Master the Art of Problem-Solving with Common Root Cause Analysis Tools and Techniques
In today’s fast-paced and complex world, problem-solving skills are crucial for success in various aspects of life. Whether you are an individual facing a personal challenge or a business trying to overcome a recurring issue, understanding the root cause of a problem is essential. This is where root cause analysis tools and techniques comes into play.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root cause analysis systematically uncovers the underlying cause or causes of a problem. It involves analyzing the problem’s symptoms and tracing them back to their root cause, rather than just addressing the symptoms themselves.
The purpose of root cause analysis is to understand why a problem occurred and to prevent its recurrence by addressing the root cause(s). Business, engineering, healthcare, and quality management are among the various fields that can utilize root cause analysis.
Understanding the concept of root cause analysis
At its core, root cause analysis aims to answer the question of “why” a problem occurs. By diving deep into the causal factors, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem and develop effective solutions.
The importance of identifying the root cause of a problem
Identifying the root cause of a problem is crucial because it allows individuals or businesses to address the core issue rather than just treating the symptoms. This approach comprehensively resolves the problem and prevents its recurrence.
Common root cause analysis techniques
There are several common root cause analysis tools that individuals or businesses can utilize to identify the underlying causes of a problem. These tools help in systematically analyzing the data and provide valuable insights, enabling informed decision-making.
Some of the most widely used techniques include the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, and Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA).
What are the Common Root Cause Analysis Tools?
Let’s take a closer look at some of the common root cause analysis tools:
Utilizing the 5 Whys technique for root cause analysis
The 5 Whys technique is a simple yet effective tool used to dig deeper into the cause-and-effect relationships of a problem. It involves asking “why” five times, peeling back the layers of symptoms to reveal the underlying root cause.
Administrating the Lean based A3 Problem Solving method
A3 Problem Solving, A systematic method rooted in Lean management, using a single-page document (A3 format) to concisely map out, analyze, and resolve complex problems, fostering root cause analysis, cross-functional collaboration, and continuous improvement.
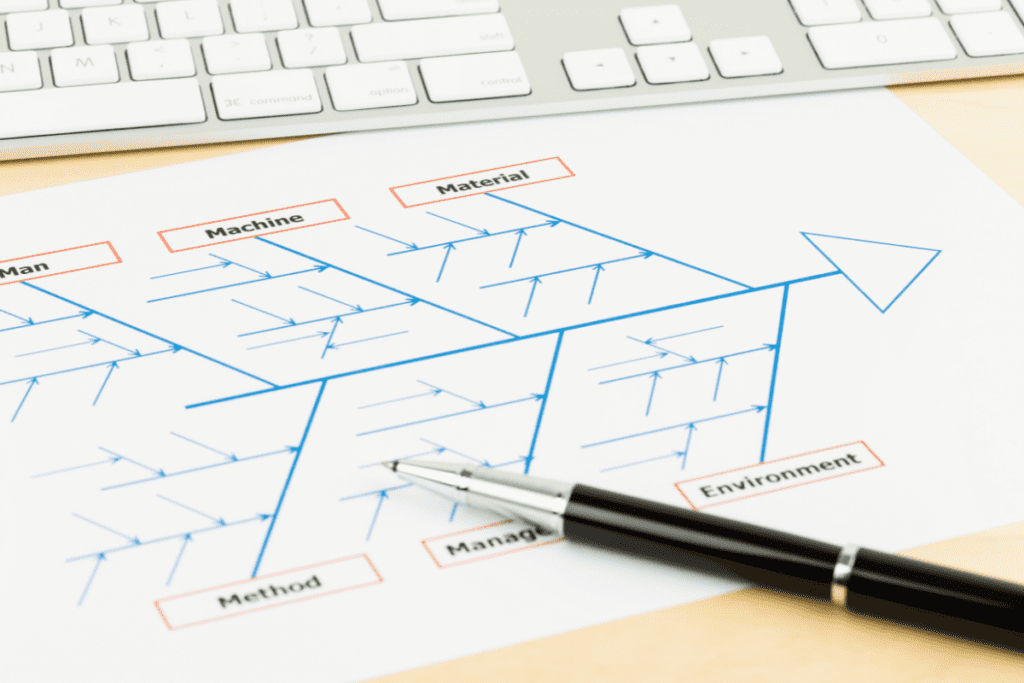
Using a Fishbone Diagram to identify potential causes
A Fishbone Diagram, also known as a cause-and-effect diagram, is a visual tool that helps identify potential causes of a problem. It categorizes the causes into different branches, such as people, processes, equipment, materials, and environment, allowing a comprehensive analysis of the problem.
Applying Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) to analyze failures
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a proactive tool used to evaluate potential failure modes and their associated effects. It helps prioritize risks and determine the potential impact of those failures, facilitating effective risk mitigation strategies.
How to effectively use Root Cause Analysis Tools?
While having access to root cause analysis tools is essential, utilizing them effectively is equally important. Here are some techniques that can help:
Using Pareto Chart to prioritize the root causes
A Pareto Chart is a bar graph that visually represents the frequency and impact of different root causes. By displaying the causes in descending order of importance, it helps focus limited resources on addressing the most critical issues first.
Implementing Fault Tree Analysis to identify failure modes
Fault Tree Analysis is a graphical tool used to identify all the possible causes that can lead to a particular problem. By visually mapping the potential failure modes, it provides a comprehensive overview of the system and helps identify the root causes effectively.
Utilizing Scatter Diagram to understand the relationship between two variables
A Scatter Diagram, also known as a scatter plot, is a graph that helps understand the relationship between two variables. It enables individuals to analyze whether changes in one variable correlate with changes in another, aiding in the identification of potential cause-and-effect relationships.
Why is Root Cause Analysis an effective problem-solving method?
Root Cause Analysis is an effective problem-solving method for several reasons:
Understanding the benefits of Root Cause Analysis in problem-solving
Root cause analysis helps individuals or organizations gain a deep understanding of the problem and its underlying causes. By addressing the root causes, it ensures a more sustainable solution that eliminates the problem entirely.
How Root Cause Analysis helps in continuous improvement
Root cause analysis is an essential tool in continuous improvement processes, such as Six Sigma. By identifying and eliminating the root causes of problems, organizations can continuously improve their operations and ensure long-term success.
Using Ishikawa Diagram to identify root causes in quality management
Quality management professionals frequently use the Ishikawa Diagram, also known as a Fishbone Diagram, to actively identify root causes. By categorizing the causes into different branches, it helps pinpoint the areas that require improvement, leading to enhanced product or service quality.
FAQs
Q: What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) serves as a method that actively identifies the cause of a problem or an undesired outcome. It helps in finding the root cause of the problem rather than just addressing its symptoms.
Q: Why is Root Cause Analysis important?
Root Cause Analysis is important because it helps in preventing the recurrence of problems. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes of a problem, organizations can implement effective solutions and improve their processes.
Q: What are the benefits of conducting Root Cause Analysis?
Conducting Root Cause Analysis offers several benefits, such as: – Identifying the core problem and its source – Preventing recurrence of the problem – Improving overall process efficiency – Enhancing quality and customer satisfaction – Implementing effective solutions – Facilitating continuous improvement
Q: What are some common Root Cause Analysis tools and techniques?
Some common Root Cause Analysis tools and techniques include:
– 5 Whys: A simple yet effective method used to ask “why” multiple times to identify the root cause of a problem.
– Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): A graphical tool used to visualize the possible causes and sub-causes of a problem.
– Pareto Chart: A bar chart that prioritizes the causes of a problem based on their frequency or impact.
-A3 Problem Solving: A systematic method rooted in Lean management, using a single-page document (A3 format) promoting root cause analysis, team collaboration, and transparent decision-making
– Scatter Diagram (Scatter Plot): A graph that shows the relationship between two variables and helps identify any correlation.
– Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA): A systematic approach to identify and mitigate potential failures in a process or system.
– Fault Tree Analysis: A technique used to analyze and determine the causes of a particular system failure or event.
Q: How does the 5 Whys method work in Root Cause Analysis?
The 5 Whys method involves asking “why” multiple times to get to the root cause of a problem. By iteratively asking why a problem occurred and identifying its underlying causes, the 5 Whys method helps in uncovering the root cause.
Q: When should Root Cause Analysis be conducted?
Whenever a significant problem or undesired outcome arises that needs addressing, conduct Root Cause Analysis. To prevent problems, perform it proactively, or use it reactively to analyze and solve existing issues.
Q: How can Root Cause Analysis be implemented effectively?
To implement Root Cause Analysis effectively, it is important to: – Clearly define the problem and its impact – Gather relevant data and information – Use the appropriate Root Cause Analysis tools and techniques – Involve a cross-functional team if necessary – Follow a structured approach and document the analysis – Implement and monitor corrective actions
Q: Can Root Cause Analysis be used for all types of problems?
Root Cause Analysis can tackle a broad spectrum of problems. However, there may be situations where a simpler approach to solving the problem is sufficient, and Root Cause Analysis tools may not be necessary.
Q: What is the difference between a Fishbone Diagram and a Pareto Chart?
A Fishbone Diagram, also known as an Ishikawa Diagram, is a visual tool used to identify and categorize the possible causes of a problem. On the other hand, a Pareto Chart is a bar chart that prioritizes the causes based on their frequency or impact. While both tools are used in Root Cause Analysis, they serve different purposes in analyzing and solving problems.
Q: How does Fault Tree Analysis contribute to Root Cause Analysis?
Fault Tree Analysis is another tool used in Root Cause Analysis. It helps in analyzing and determining the causes of a particular system failure or event. By identifying the contributing factors and their relationships, Fault Tree Analysis can assist in finding the root cause of a problem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of problem-solving requires the effective utilization of root cause analysis tools.
By understanding and utilizing techniques such as the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, Pareto Chart, Fault Tree Analysis, and Scatter Diagram,
Individuals and organizations can successfully identify the root causes of problems and take appropriate actions to prevent their recurrence.
Root cause analysis is an essential tool in continuous improvement and quality management, helping to drive successful problem-solving and ensure long-term success.
If you liked this article, remember to subscribe to MiamiCloud.com. Connect. Learn. Innovate.